Popular Instructors
All JPNPP: Theory & Pedagogy Courses
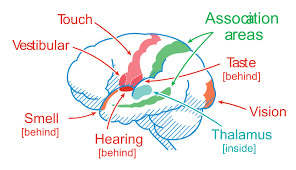
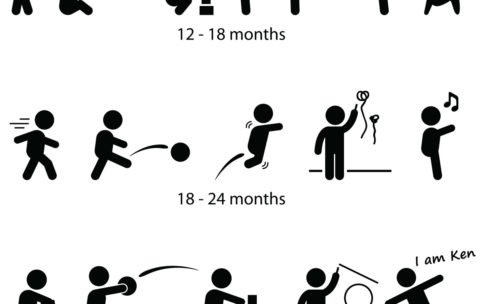
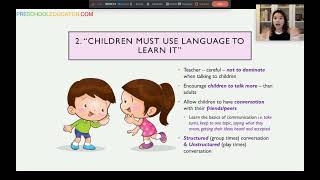
JPNPP Series: Learning Through Play by Datin Indranee Liew (Part 1)
Learning through play is crucial for children’s development, offering them …
What you'll learn
It enables parents, caregivers, and educators to appreciate the importance of play in children's development, encouraging them to prioritise and facilitate play opportunities.
It empowers adults to create environments and experiences that optimise learning and growth.
Learning what children learn through play contributes to more effective parenting, teaching, and caregiving practices, enhancing child development outcomes.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 7) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 6) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 5) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 4) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 3) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 2) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.
JPNPP Series: An Overview of Promoting Social-Emotional Well-Being of Educators in an Early Childhood Setting – A Practical Guide (Part 1) by Mohan Dallumal
Promoting the social-emotional well-being of educators in early childhood settings …
What you'll learn
Positive Role Modeling: Educators prioritising their social-emotional well-being serve as positive role models for young children. By demonstrating healthy coping mechanisms, emotional regulation skills, and positive interpersonal relationships, educators help children develop similar behaviours.
Improved Classroom Environment: Educators with strong social-emotional well-being create a more positive and supportive classroom environment. This environment encourages trust, empathy, and open student communication, leading to better collaboration and learning outcomes.
Enhanced Student-Teacher Relationships: Educators who understand the importance of their social-emotional well-being are better equipped to build strong relationships with their students. These relationships are foundational for effective teaching and learning, fostering students' sense of belonging and security.
Reduced Burnout and Turnover: Prioritising social-emotional well-being helps prevent burnout and turnover among educators. By managing stress, maintaining work-life balance, and seeking support, educators can sustain their passion for teaching and remain committed to their profession in the long term.
Optimised Professional Growth: Understanding the importance of social-emotional well-being supports educators' ongoing professional growth. By engaging in self-reflection, seeking professional development opportunities, and fostering a supportive network, educators continuously improve their teaching practices and contribute to their success and that of their students.